双模态跨语料库语音情感识别
摘要: 语音情感识别(SER)在双模态的跨数据库语音情感识别研究较少,跨数据库情感识别过度减少数据集之间差异的同时,会忽视情感判别能力的特征的问题。YouTube数据集为源数据,互动情感二元动作捕捉数据库(IEMOCAP)为目标数据。在源数据和目标数据中,Opensmile工具箱用来提取语音特征,将提取的语音特征输入到CNN和双向长短期记忆网络(BLSTM),来提取更高层次的特征,文本模态为语音信号的翻译稿。首先双向编码器表示转换器(Bert)把文本信息向量化,BLSTM提取文本特征,然后设计模态不变损失来形成2种模态的公共表示空间。为了解决跨语料库的SER问题,通过联合优化线性判别分析(LDA)、最大平均差异(MMD)、图嵌入(GE)和标签回归(LSR),学习源数据和目标数据的公共子空间。为了保留情绪辨别特征,情感判别损失与MMD+GE+LDA+LSR相结合。SVM分类器作为迁移公共子空间的最终情感分类,IEMOCAP上的实验结果表明,此方法优于其他先进的跨语料库和双模态SER.
Abstract: In the field of speech emotion recognition(SER), a heterogeneity gap exists between different modalities and most cross-corpus SER only uses the audio modality. These issues were addressed simultaneously. YouTube datasets were selected as source data and an interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database (IEMOCAP) as target data. The Opensmile toolbox was used to extract speech features from both source and target data, then the extracted speech features were input into Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and bidirectional long short-term memory network (BLSTM) to extract higher-level speech features with the text mode as the translation of speech signals. Firstly, BLSTM was adopted to extract the text features from text information vectorized by Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers (BERT), then modality-invariance loss was designed to form a common representation space for the two modalities. To solve the problem of cross-corpus SER, a common subspace of source data and target data were learned by optimizing Linear Discriminant analysis (LDA), Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) and Graph Embedding (GE) and Label Smoothing Regularization (LSR) jointly. To preserve emotion-discriminative features, emotion-aware center loss was combined with MMD+GE+LDA+LSR. The SVM classifier was designed as a final emotion classification for migrating common subspaces. The experimental results on IEMOCAP showed that this method outperformed other state-of-art cross-corpus and bimodal SER.
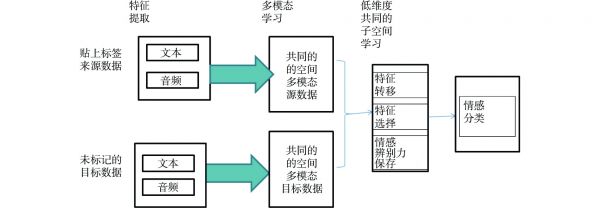
图 1 BMTDAFSL的方法的结构
Figure 1. The structure of BMTDAFSL
表 1 实验参数
Table 1 Experiment parameters
参数价值 dropout0. 5学习率0. 001批量大小64循环次数10BLSTM隐层节点数128多头注意机制的头数8表 2 与双模态SER和仅使用音频模态或文本模态的方法的其他先前工作的比较。
Table 2 Comparison with other previous work on bimoal SER and our method of using only audio mode or text mode
方法准确性/% 文献[3]75. 23文献[4]71. 86文献 [26]78. 25本文方法(音频)76. 74本文方法(文本)80. 69本文方法(音频+文本)87. 03表 3 与以前跨语料库情感识别的比较
Table 3 Comparison with other previous work on cross-corpus ser
方法准确性/% 文献[13]69. 23文献[16]72. 56文献[14]72. 84本文方法87. 03 [1]KOROMILAS P,GIANNAKOPOULOS T. Deep multimodal emotion recognition on human speech: a review[J]. Applied Sciences,2021,11(17): 7962.
[2]WEN H,YOU S,FU Y. Cross-modal dynamic convolution for multi-modal emotion recognition[J]. Journal of Communication and Image Representation,2021(78): 103178.
[3]SINGH P,SRIVASTAVA R,RANA K P S,et al. A multimodal hierarchical approach to speech emotion recognition from audio and text[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems,2021(229): 107316.
[4]CAI L,HU Y,DONG J,et al. Audio-textual emotion recognition based on improved neural networks[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering,2019(6): 1-9.
[5]WANG X S,CHEN X,CAO C. Human emotion recognition by optimally fusing facial expression and speech feature[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication,2020(84): 115831.
[6]WANG M,HUANG Z,LI Y,et al. Maximum weight multi-modal information fusion algorithm of electroencephalographs and face images for emotion recognition[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering,2021(94): 107319.
[7]ZHANG H,HUANG H,HAN H. A Novel heterogeneous parallel convolution Bi-LSTM for speech emotion recognition[J]. Applied Sciences,2021,11(21): 9897.
[8]CHEN G H, ZENG X P. Multi-modal emotion recognition by fusing correlation features of speech-visual[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters,2021(28): 533-537.
[9]ZHANG S,CHEN M,CHEN J,et al. Combining cross-modal knowledge transfer and semi-supervised learning for speech emotion recognition[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems,2021(229): 107340.
[10]DONG G N,PUN C M,ZHANG Z. Temporal relation inference network for multi-modal speech emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactionsfor Circuits and Systems for Video Technology,2022,32(9): 6472-6485.
[11]LI C,BAO Z,LI L,et al. Exploring temporal representations by leveraging attention-based bidirectional LSTM-RNNs for multi-modal emotion recognition[J]. Information Processing and Management,2020,57(3): 102185.
[12]LU C,ZONG Y,TANG C,et al. Implicitly aligning joint distributions for cross-corpus speech emotion recognition[J]. Electronics,2022,11(17): 2745.
[13]LIU N,ZHANG B,LIU B,et al. Transfer subspace learning for unsupervised cross-corpus speech emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Access,2021(9): 95925-95937.
[14]LI S,SONG P,ZHANG W. Transferable discriminant linear regression for cross-corpus speech emotion recognition[J]. Applied Acoustics,2022(197): 108919.
[15]SONG P,OU S,DU Z,et al. Learning corpus-invariant discriminant feature representations for speech emotion recognition[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems,2017,100(5): 1136-1139.
[16]ZHANG W,SONG P. Transfer sparse discriminant subspace learning for cross-corpus speech emotion recognition[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio Speech and Language Processing,2019(28): 307-318.
[17]OCQUAYE E N N,MAO Q,SONG H,et al. Dual exclusive attentive transfer for unsupervised deep convolutional domain adaptation in speech emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Access,2019(7): 93847-93857.
[18]SONG P,ZHENG W,OU S,et al. Cross-corpus speech emotion recognition based on transfer non-negative matrix factorization[J]. Speech Communication,2016(83): 34-41.
[19]FU C,LIU C,ISHI C T,et al. Multi-modality emotion recognition model with GAT-based multi-head inter-modality attention[J]. Sensors,2020,20(17): 4894. DOI: 10.3390/s20174894
[20]LIU D,ChEN L,WANG Z,et al. Speech expression multimodal emotion recognition based on deep belief network[J]. Journal of Grid Computing,2021,19(2): 22. DOI: 10.1007/s10723-021-09564-0
[21] 程大雷,张代玮,陈雅茜. 多模态情感识别综述[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2022(4): 048. [22]GUO L,WANG L,DANG J,et al. Emotion recognition with multimodal transformer fusion framework based on acoustic and lexical information[J]. IEEE Multimedia,2022,29(2): 94-103. DOI: 10.1109/MMUL.2022.3161411
[23]ZOU S H,HUANG X,SHEN X D,et al. Improving multimodal fusion with main modal transformer for emotion recognition in conversation[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems,2022(258): 109978.
[24]CAO X,JIA M S,RU J W,et al. Cross-corpus speech emotion recognition using subspace learning and domain adaption[J]. EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing,2022(32): 00264.
[25]PHAN D A,MATSUMOTO Y,SHINDO H. Autoencoder for semi-supervised multiple emotion detection of conversation transcripts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing,2018,12(3): 682-691.
[26]DENG J,ZHANG Z,EYBEN F,et al. Autoencoder-based unsupervised domain adaptation for speech emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters,2014,21(9): 1068-1072. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2324759
[27]SONG P,OU S,DU Z,et al. Learning corpus-invariant discriminant feature representations for speech emotion recognition[J]. Speech Communication,2018(99): 1136-1139.
[28]CHEN X,ZHOU X,LU C,et al. Target-adapted subspace learning for cross-corpus speech emotion recognition[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems,2019,102(12): 80-89.
[29]ZHEN L,HU P,PENG X,et al. Deep multimodal transfer learning for cross-modal retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2020,33(2): 798-810.
[30]MAO Q,XU G,XUE W,et al. Learning emotion-discriminative and domain-invariant features for domain adaptation in speech emotion recognition[J]. Speech Communication,2017(93): 1-10.
[31]LU C,TANG C,ZHANG J,et al. Progressively discriminative transfer network for cross-corpus speech emotion recognition[J]. Entropy,2022,24(8): 1046.
[32]HO N H,YANG H J,KIM S H,et al. Multimodal approach of speech emotion recognition using multi-level multi-head fusion attention-based recurrent neural network[J]. IEEE Access,2020(8): 61672-61686.
相关知识
语音识别
CTI论坛: 认准语音识别的“内核”
语音识别抑郁症的关键技术研究
“全球健康传播”双语平行语料库正式发布!
电话语音识别/114查号
语音识别在移动医疗领域的探索
【Android语音合成与语音识别】
全球健康传播双语平行语料库正式发布
语音识别在移动医疗app中的应用
眼部按摩仪语音控制方案:NRK3301语音识别芯片
网址: 双模态跨语料库语音情感识别 https://www.trfsz.com/newsview681922.html
推荐资讯
- 1发朋友圈对老公彻底失望的心情 12775
- 2BMI体重指数计算公式是什么 11235
- 3补肾吃什么 补肾最佳食物推荐 11199
- 4性生活姿势有哪些 盘点夫妻性 10428
- 5BMI正常值范围一般是多少? 10137
- 6在线基础代谢率(BMR)计算 9652
- 7一边做饭一边躁狂怎么办 9138
- 8从出汗看健康 出汗透露你的健 9063
- 9早上怎么喝水最健康? 8613
- 10五大原因危害女性健康 如何保 7828






